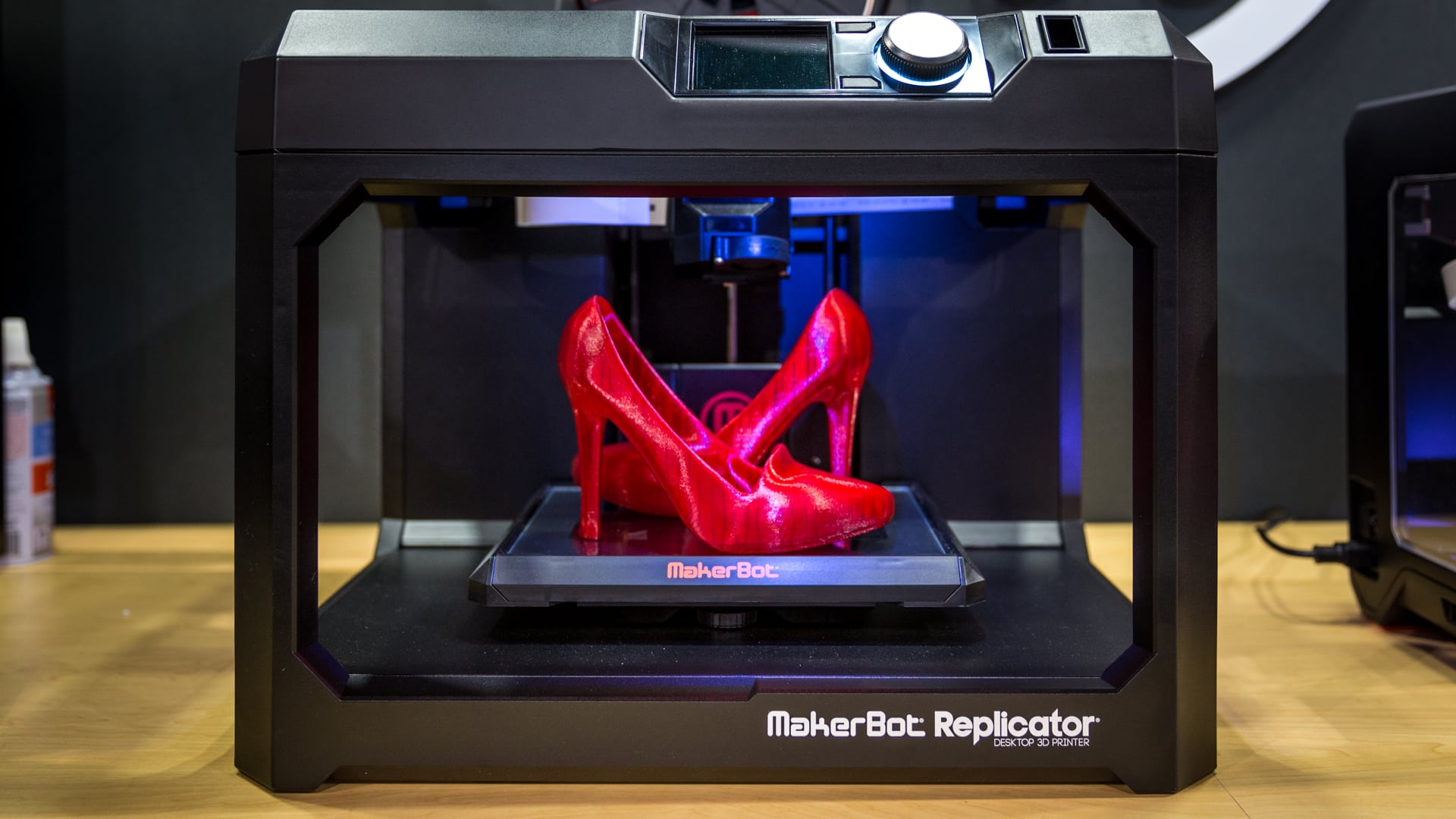
Types of 3D Printers
3D Printers for various applications and usesDigital Light Processing (DLP)
Similar to SLA printers, DLP uses a digital light projector to create a complete image of an entire layer all at once. Because DLP does an entire image, it is faster than SLA printers, which traces or outlines the pattern with a laser beam.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) /Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Selective Laser Melting or Direct Metal Laser Sintering is a rapid Oil&Gas, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing technique designed to use a high power-density laser to melt and fuse metallic powders together.
Directed Energy Deposition (DED)
Directed Energy Deposition (DED) is an additive manufacturing process where metal wire or powder is combined with an energy source to deposit material onto a build tray or an existing part directly.
Drop on Demand (DOD)
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Electron Beam Melting uses a powder from the printer powder bed. The powder is deposited in thin layers that are preheated and then melted layer-by-layer to create the model. A high energy electron beam, thus the name, is used to harden and solidify the metal.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM printers are fairly simple, made up of primarily two parts: a platform extrusion nozzle and a control system that allows a quick and simple means to getting started in 3D printing.
Metal Binder Jetting (MBJ)
In MBJ, a metal powder is used in the creation of the object. Using a polymer binding agent, the metal powder is bound together. The metal objects created using MBJ can be much more complex than is possible with prior manufacturing processes.
Sand Binder Jetting (SBJ)
As the name implies, Sand Binder jetting uses sand, typically sandstone or gypsum, to produce parts. SBJ is used frequently for creating molds and cores that are then used for casting,
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS uses the laser to solidify and bind together the various granular materials laid down in a powder form that are used in producing the project. The laser traces out the pattern for each layer, as does SLA, but then lowers the bed to create another layer. This means that SLS printing doesn’t need or require a support mechanism for complex structures.
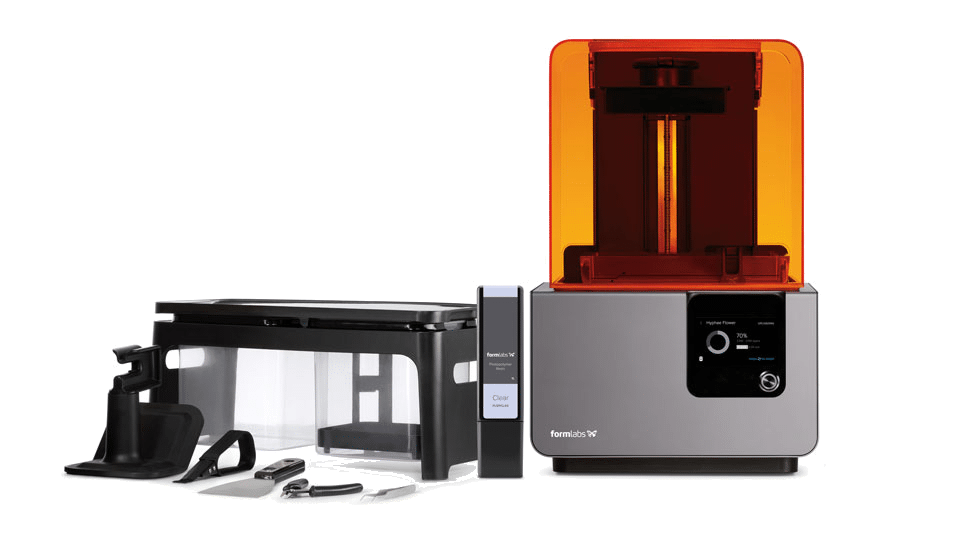
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA is the oldest 3D printing technology. Stereolithography printing lays down the resin and then hits the resin with a UV-laser beam which hardens the pattern just laid down and then the process is repeated and the item is built layer upon layer.
Sheet Lamination
Sheet lamination processes include ultrasonic additive manufacturing (UAM) and laminated object manufacturing (LOM). The Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing process uses sheets or ribbons of metal, which are bound together using ultrasonic welding.