In the recently published ‘ Three Dimensional Digital Alloying with Reactive Metal Inks ,’ author Chaitanya G. Mahajan submitted a dissertation for a PhD at the Kate Gleason College of Engineering at the Rochester Institute of Technology, exploring new ways to 3D print multifunctional components with multiple materials.
.
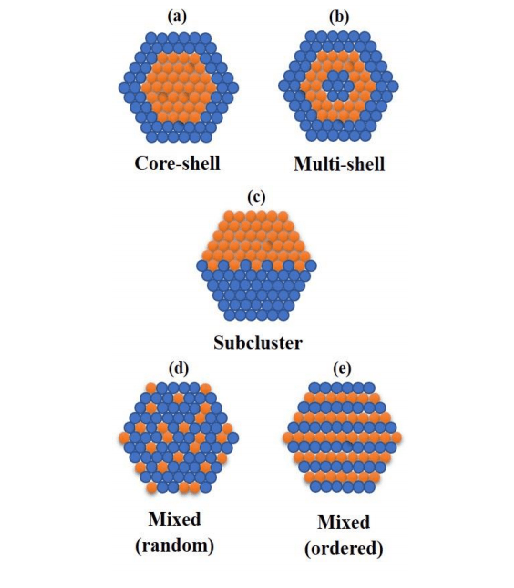
Mahajan extensively explores the theory of nanoalloys, including details on core-shell nanoalloys, subcluster nanoalloys, mixed nanoalloys, multishell nanoalloys, along with the factors influencing their structure from strength of atomic bonding to surface energies of bulk elements, atomic size, and more. The author discusses the variety of nanoalloys, created via a chemical, bottom-up method, as well as a physical top-down method. With bulk metal broken into nanosized particles for the top-down technique, for bottom-up, both atoms and molecules are brought together to construct nanoparticles. “The main advantage of the top-down approaches is that bulk quantities of nanoparticles can be produced within […]
Case Study: How PepsiCo achieved 96% cost savings on tooling with 3D Printing Technology
Above: PepsiCo food, snack, and beverage product line-up/Source: PepsiCo PepsiCo turned to tooling with 3D printing...


























0 Comments