NASA ‘s renewed efforts to return humans to the moon by 2024 has led to advances in new space technologies to improve processes, and reduce costs and development time.
.
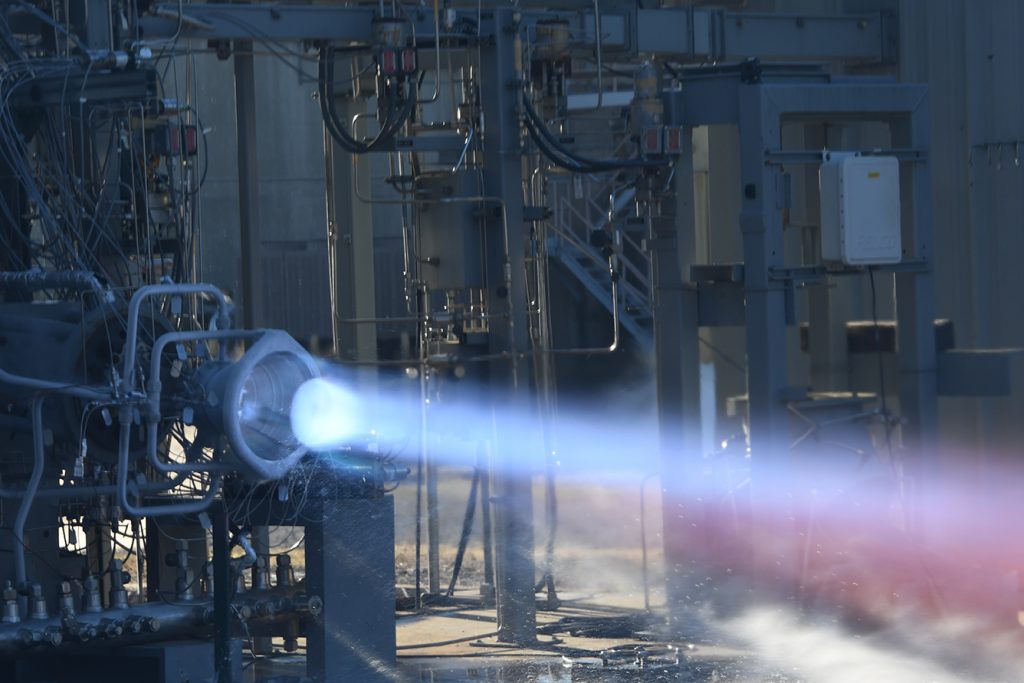
In early December 2020, we learned that engineers at the U.S. space agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama successfully hot-fire tested 3D printed components for rocket engines. The copper alloy combustion chamber and nozzle were made of a high-strength, hydrogen-resistant alloy and could withstand the same extreme combustion environments that traditionally manufactured metal structures experience in flight.
.
This huge milestone could pave the way for 3D printed parts aboard new rockets.
.
“This 3D printed technology is a game-changer when it comes to reducing total hardware manufacturing time and cost,” said Thomas Teasley, a test engineer at NASA’s Marshall Center. “These hot-fire tests are a critical step in preparing this hardware for use in future Moon and Mars missions.” Teasley worked with a team of Marshall test engineers to prove how good these 3D printed parts are. For the task, they performed 23 hot-fire tests for a total duration of 280 seconds over 10 test days. Throughout the testing, engineers collected data, including pressure and temperature measurements in hardware […]
Case Study: How PepsiCo achieved 96% cost savings on tooling with 3D Printing Technology
Above: PepsiCo food, snack, and beverage product line-up/Source: PepsiCo PepsiCo turned to tooling with 3D printing...


























0 Comments